本文介绍Flink在流计算场景的简单应用,实时消费SLS内的AccessLog,并将计算结果输出到Elasticsearch。
环境
- Flink
- 1.8
- ES
- 6.3.2
假设场景
日志结构
request_time: 1556415329
uri: /analysis/path?id=1
系统AccessLog通过Logtai采集到阿里云SLS,指定request_time为日志时间字段。示例场景需求统计指定uri.path+uri.query.id分组统计访问计数。
- 实时消费
SLS日志 - 筛选
uri.path=/analysis/path(简化只统计单个path,实际场景可能是多个path的访问统计,相应的key参数规则也会不同) - 解析
uri.query参数id
创建ES索引
PUT sls_analysis
PUT sls_analysis/_mapping/_doc
{
"properties": {
"path": {
"type": "text"
},
"key": {
"type": "integer"
},
"count": {
"type": "integer"
},
"timestamp": {
"type":"long"
}
}
}
流程解析
接下来结合hb-chen/flink-practice源码对流程进行解析。
Gradle添加依赖
// ES
flinkShadowJar "org.apache.flink:flink-connector-elasticsearch6_${scalaBinaryVersion}:${flinkVersion}"
// SLS
flinkShadowJar "com.aliyun.openservices:flink-log-connector:0.1.7"
flinkShadowJar "com.aliyun.openservices:aliyun-log:0.6.19"
flinkShadowJar "com.aliyun.openservices:log-loghub-producer:0.1.8"
flinkShadowJar "com.google.protobuf:protobuf-java:2.5.0"
// YAML解析
flinkShadowJar "org.yaml:snakeyaml:1.24"
参数&配置(可忽略)
虽然只是示例还是做了args参数及config.yml配置的获取,方便配置
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
final ParameterTool params = ParameterTool.fromArgs(args);
String analysisPath = params.getRequired("path");
String analysisQueryKey = params.get("key", "id");
LOG.info("access log analysis path:" + analysisPath + " key:" + analysisQueryKey);
Config config = getConfig();
// ……
}
private static Config getConfig() {
Constructor constructor = new Constructor(Config.class);
org.yaml.snakeyaml.Yaml yaml = new org.yaml.snakeyaml.Yaml(constructor);
Config config = yaml.loadAs(SlsAnalysis.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("config.yml"), Config.class);
return config;
}
日志消费
首先参考官方文档通过SLS的各种配置创建一个Consumer,获得SLS日志流DataStream<RawLogGroupList> logStream
// SLS消费
// https://help.aliyun.com/document_detail/63594.html
Properties configProps = new Properties();
// 设置访问日志服务的域名
configProps.put(ConfigConstants.LOG_ENDPOINT, config.getSls().getEndpoint());
// 设置访问ak
configProps.put(ConfigConstants.LOG_ACCESSSKEYID, config.getSls().getAk());
configProps.put(ConfigConstants.LOG_ACCESSKEY, config.getSls().getSk());
// 设置日志服务的project
configProps.put(ConfigConstants.LOG_PROJECT, config.getSls().getProject());
// 设置日志服务的Logstore
configProps.put(ConfigConstants.LOG_LOGSTORE, config.getSls().getLogStore());
// 设置消费日志服务起始位置
configProps.put(ConfigConstants.LOG_CONSUMER_BEGIN_POSITION, "" + (System.currentTimeMillis() / 1000L));
// 设置日志拉取时间间隔及每次调用拉取的日志数量
configProps.put(ConfigConstants.LOG_FETCH_DATA_INTERVAL_MILLIS, "1000");
configProps.put(ConfigConstants.LOG_MAX_NUMBER_PER_FETCH, "100");
// 设置Shards发现周期
configProps.put(ConfigConstants.LOG_SHARDS_DISCOVERY_INTERVAL_MILLIS, Consts.DEFAULT_SHARDS_DISCOVERY_INTERVAL_MILLIS);
// 设置日志服务的消息反序列化方法
RawLogGroupListDeserializer deserializer = new RawLogGroupListDeserializer();
final StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
DataStream<RawLogGroupList> logStream = env.addSource(new FlinkLogConsumer<RawLogGroupList>(deserializer, configProps));
通过RawLogGroupList结构知道logStream获得的是批量的SLS日志,单条日志是分组的RawLog列表,这就需要首先对批量的数据进行展开(flatMap())来获得单条数据流
public class RawLogGroupList implements Serializable {
public List<RawLogGroup> rawLogGroups = new ArrayList();
}
public class RawLogGroup implements Serializable {
public String source;
public String topic = "";
public Map<String, String> tags = new HashMap();
public List<RawLog> logs = new ArrayList();
}
批量日志展开
这是整个过流程最关键的一环,这里要定义展开后数据流的结构,不啰嗦直接看结构Tuple4<AccessLogAnalysis, Integer, Long, Long>
f0:AccessLogAnalysis是解析uri的path+key的对象,也就是要用做keyBy的属性f1:Integer统计数量,单条日志全计为1(根据需求这里可以考些优化,比如Group内有序可以在range过程直接对相同request_time做聚合)f2:Long日志时间戳,考虑后续作为EventTime使用,所以将request_time转为毫秒f3:Long批量日志的最小时间戳,因为SLS日志是时间有序的,且单个RawLogGroup日志升序,所以自然的考虑使用最小时间戳作为watermark,这样也避免了arrive late的出现
// SLS批量日志展开
DataStream<Tuple4<AccessLogAnalysis, Integer, Long, Long>> flatStream = logStream.flatMap(new FlatMapFunction<RawLogGroupList, Tuple4<AccessLogAnalysis, Integer, Long, Long>>() {
@Override
public void flatMap(RawLogGroupList value, Collector<Tuple4<AccessLogAnalysis, Integer, Long, Long>> out) throws Exception {
// Log group内时间升序,记录所有分组最小时间戳,即为watermark位置
long minTimestamp = Long.MAX_VALUE;
for (RawLogGroup group : value.getRawLogGroups()) {
if (group.getLogs().size() > 0) {
RawLog log = group.getLogs().get(0);
long rt = Optional.ofNullable(log.getContents().get("request_time")).map(Long::new).orElse(Long.MAX_VALUE);
minTimestamp = rt < minTimestamp ? rt : minTimestamp;
}
}
// 取毫秒,排除MAX_VALUE
minTimestamp = minTimestamp == Long.MAX_VALUE ? minTimestamp : minTimestamp * 1000;
Integer count = 0;
for (RawLogGroup group : value.getRawLogGroups()) {
count += group.getLogs().size();
for (RawLog log : group.getLogs()) {
// URI解析
QueryStringDecoder decoder = new QueryStringDecoder(log.getContents().get("uri"));
String path = decoder.path();
List<String> keyList = decoder.parameters().get(analysisQueryKey);
if (path.equalsIgnoreCase(analysisPath) && keyList != null && keyList.size() > 0) {
Integer id = Optional.ofNullable(keyList.get(0)).map(Integer::new).orElse(0);
AccessLogAnalysis ala = new AccessLogAnalysis();
ala.setKey(id);
ala.setPath(path);
Long timestamp = Optional.ofNullable(log.getContents().get("request_time")).map(Long::new).orElse(0L);
timestamp *= 1000;
out.collect(new Tuple4<>(ala, 1, timestamp, minTimestamp));
}
}
}
LOG.info("raw log count:" + count + " timestamp:" + minTimestamp);
}
});
EventTime & timeWindow
有了flatStream的结果,自定义EventTime以及Watermark就比较简单。.keyBy(0).timeWindow(Time.seconds(60)).sum(1)流程以f0为key分隔,60s为时间窗口对f1求和。
DataStream result = flatStream.assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(new AssignerWithPunctuatedWatermarks<Tuple4<AccessLogAnalysis, Integer, Long, Long>>() {
@Nullable
@Override
public Watermark checkAndGetNextWatermark(Tuple4<AccessLogAnalysis, Integer, Long, Long> lastElement, long extractedTimestamp) {
return lastElement.f3 <= extractedTimestamp ? new Watermark(lastElement.f3) : null;
}
@Override
public long extractTimestamp(Tuple4<AccessLogAnalysis, Integer, Long, Long> element, long previousElementTimestamp) {
if (element.f2 > 0L) {
return element.f2;
} else {
return previousElementTimestamp;
}
}
})
.keyBy(0)
.timeWindow(Time.seconds(60))
.sum(1);
输出到ES
大致参考官方文档即可, 只是没有认证(生产环境必不可少,想到ES社区的分享,在shodan.io上找各种公开免费ES资源😏)
// Sink:Elasticsearch
List<HttpHost> httpHosts = new ArrayList<>();
httpHosts.add(new HttpHost(config.getEs().getHostname(), 9200, "http"));
// use a ElasticsearchSink.Builder to create an ElasticsearchSink
ElasticsearchSink.Builder<Tuple4<AccessLogAnalysis, Integer, Long, Long>> esSinkBuilder = new ElasticsearchSink.Builder<>(httpHosts, new ElasticsearchSinkFunction<Tuple4<AccessLogAnalysis, Integer, Long, Long>>() {
public IndexRequest createIndexRequest(Tuple4<AccessLogAnalysis, Integer, Long, Long> element) {
Map<String, String> json = new HashMap<>();
json.put("path", element.f0.getPath());
json.put("key", element.f0.getKey().toString());
json.put("count", element.f1.toString());
json.put("timestamp", element.f3.toString());
return Requests.indexRequest().index("sls_analysis").type("_doc").source(json);
}
@Override
public void process(Tuple4<AccessLogAnalysis, Integer, Long, Long> element, RuntimeContext runtimeContext, RequestIndexer requestIndexer) {
requestIndexer.add(createIndexRequest(element));
}
});
// configuration for the bulk requests; this instructs the sink to emit after every element, otherwise they would be buffered
esSinkBuilder.setBulkFlushMaxActions(1);
// provide a RestClientFactory for custom configuration on the internally created REST client
String esUsername = config.getEs().getUsername();
String esPassword = config.getEs().getPassword();
esSinkBuilder.setRestClientFactory(restClientBuilder -> {
// restClientBuilder.setDefaultHeaders(headers);
// restClientBuilder.setMaxRetryTimeoutMillis(...)
// restClientBuilder.setPathPrefix(...)
restClientBuilder.setHttpClientConfigCallback(new RestClientBuilder.HttpClientConfigCallback() {
@Override
public HttpAsyncClientBuilder customizeHttpClient(HttpAsyncClientBuilder httpAsyncClientBuilder) {
CredentialsProvider credentialsProvider = new BasicCredentialsProvider();
credentialsProvider.setCredentials(AuthScope.ANY, new UsernamePasswordCredentials(esUsername, esPassword));
return httpAsyncClientBuilder.setDefaultCredentialsProvider(credentialsProvider);
}
});
});
// finally, build and add the sink to the job's pipeline
result.addSink(esSinkBuilder.build());
这里还遇到个小坑(Java丢的太久了😂),在UsernamePasswordCredentials()中直接使用config.getEs().getUsername() config.getEs().getPassword(),导致序列化错误,相关参考Apache Flink#踩过的坑
Exception in thread "main" org.apache.flink.api.common.InvalidProgramException: The implementation of the ElasticsearchSinkBase is not serializable. The object probably contains or references non serializable fields.
测试 & 打包
# 测试
$ ./gradlew sls:run --args="--path /analysis/path"
# 打包
$ ./gradlew clean sls:shadowJar
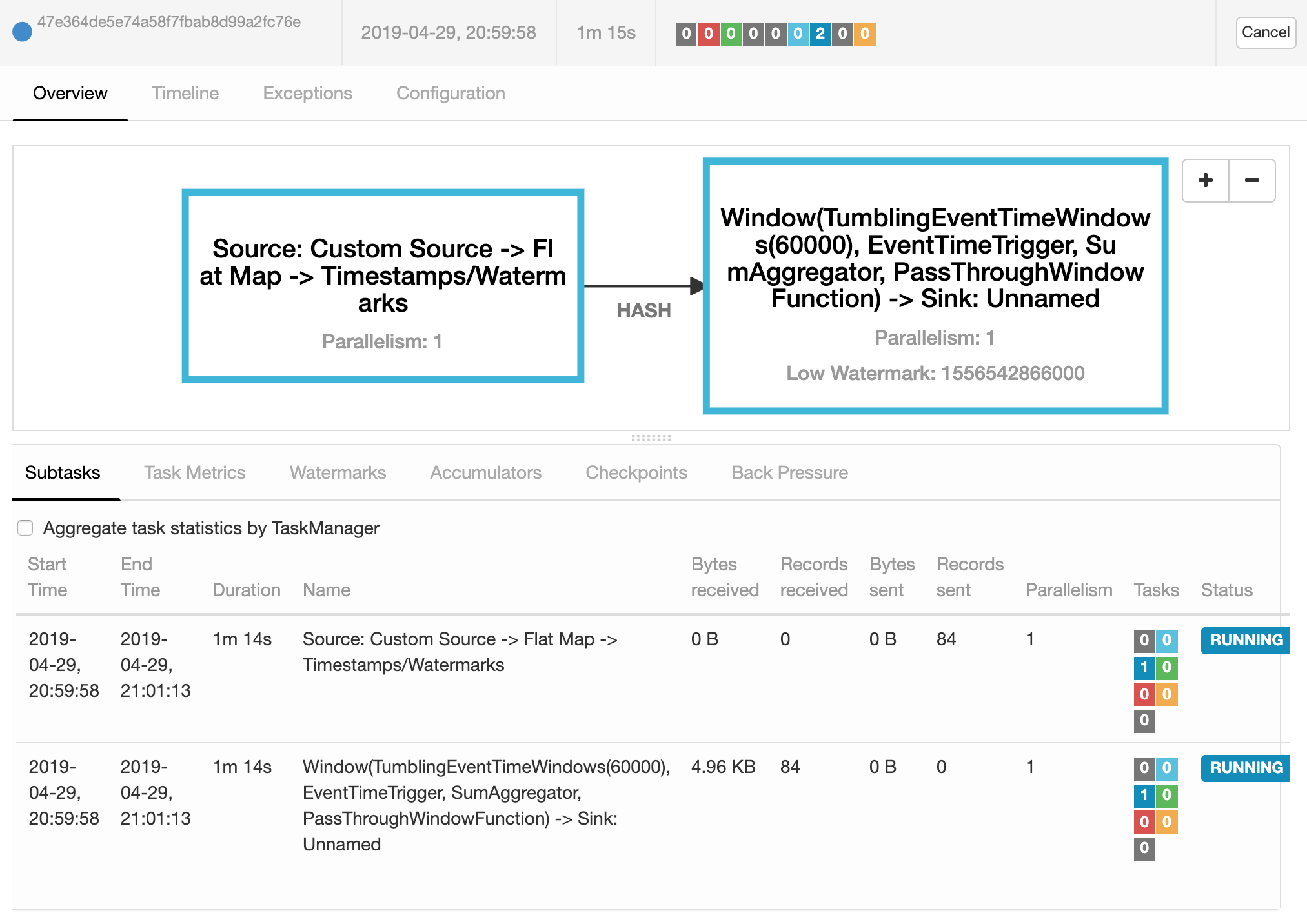
提交Job到Flink运行
上传.jar到Flink
Program Arguments
--path /analysis/path
到Kibana看下结果
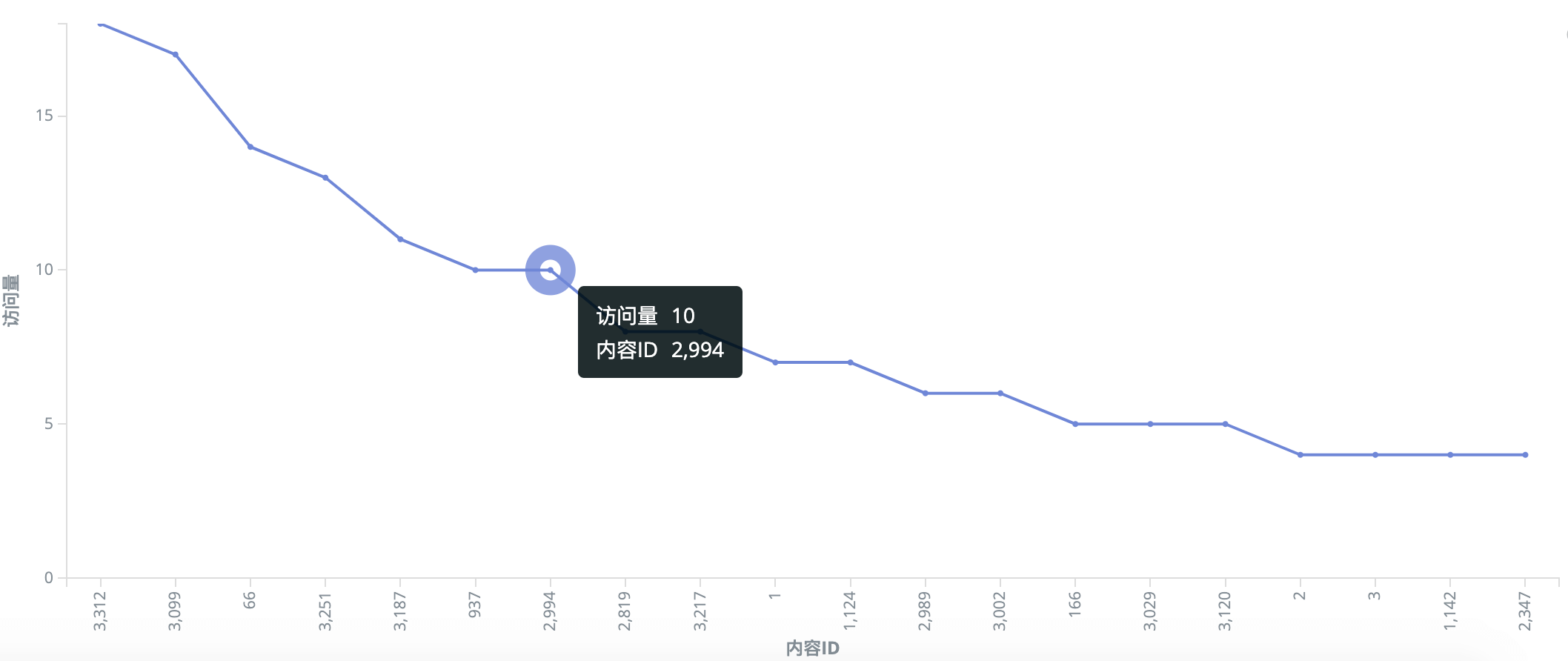
GET /sls_analysis/_search
{
"aggs": {
"2": {
"terms": {
"field": "key",
"size": 20,
"order": {
"1": "desc"
}
},
"aggs": {
"1": {
"sum": {
"field": "count"
}
}
}
}
},
"size": 0,
"_source": {
"excludes": []
},
"stored_fields": [
"*"
],
"script_fields": {},
"docvalue_fields": [],
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"match_all": {}
},
{
"match_phrase": {
"path": {
"query": "/analysis/path"
}
}
}
],
"filter": [],
"should": [],
"must_not": []
}
}
}
TODO
- Checkpoint